Desarrollo de un Sistema Adaptativo de Adquisición y Transmisión para el Procesamiento Digital de Señales de ECG Bajo Esquemas Variables n-QAM
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.44.4.8Palabras clave:
ECG, n-QAM, RF, telemedicina, transceptorResumen
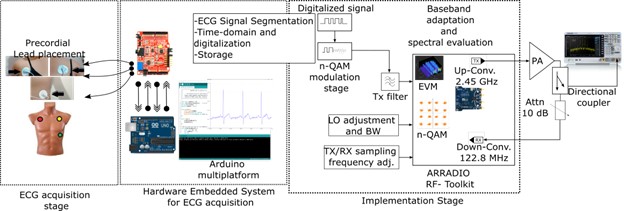
El monitoreo y transmisión de señales biomédicas, particularmente ECG, es fundamental en la era pospandemia, este trabajo de investigación se centra en el desarrollo de una plataforma para la adquisición, adaptación y transmisión de señales bajo diversos esquemas de modulación n-QAM. El sistema incluye una etapa de adquisición mediante el módulo Olimex y electrodos con un sensor tipo Ag/AgCl. Se desarrolló un algoritmo adaptativo a los diversos esquemas de modulación n-QAM para la gestión de anchos de banda apropiados durante una implementación en la banda de 2,5 GHz, al amplificador de potencia se operó en la región lineal para mejorar el factor de cresta y obtener un ACPR cercano a 30 dBc, se realizó una demodulación adecuada de la señal ECG y es posible migrar a esquemas de modulación superiores a 64-QAM si se requiere detectar altas frecuencias y un posterior análisis de Fourier. El sistema desarrollado como propuesta de Telemedicina brinda versatilidad para la adquisición de señales, digitalización, almacenamiento de datos y un esquema multivariable n-QAM, la implementación en hardware proporcionó una adecuada adaptabilidad para esquemas n-QAM. El sistema se implementó sobre un transceptor AD9361 que elimina el tradicional generador vectorial de señal y permite un control óptimo de los tonos a enviar, para aporte en el área de Telemedicina a través de transmisión RF.
Descargas
Citas
World Health Organization, “Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs),” WHO. 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
A. Ibaida, A. Abuadbba, N. Chilamkurti, “Privacy-preserving compression model for efficient IoMT ECG sharing,” Comput. Commun., vol. 166, no. 15, pp. 1-8, Jan. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.11.010
C. De Capua, A. Meduri and R. Morello, “A Smart ECG Measurement System Based on Web-Service-Oriented Architecture for Telemedicine Applications,” IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 59, no. 10, pp. 2530-2538, Oct. 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2010.2057652
J. Francis, “ECG monitoring leads and special leads,” Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J., vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 92–95, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipej.2016.07.003
I. -A. Ivanciu, L. Ivanciu, D. Zinca, and V. Dobrota, “Securing Health-Related Data Transmission Using ECG and Named Data Networks,” in 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Local and Metropolitan Area Networks (LANMAN), Paris, France, 2019, pp. 1-6, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LANMAN.2019.8846993
M. Zulqarnain, S. Stanzione, G. Rathinavel, S. Smout, M. Willegems, K. Myny, and E. Cantatore, “A flexible ECG patch compatible with NFC RF communication,” npj Flex. Electron., vol. 4, art. no. 13, Jul. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-020-0077-x
Y. Cho, H. Shin, and K. Kang, “Scalable Coding and Prioritized Transmission of ECG for Low-Latency Cardiac Monitoring Over Cellular M2M Networks,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 8189-8200, Jan. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2795028
N. Clark, E. Sandor, C. Walden, I. S. Ahn and Y. Lu, “A wearable ECG monitoring system for real-time arrhythmia detection,” in 2018 IEEE 61st International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Windsor, ON, Canada, 2018, pp. 787-790, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MWSCAS.2018.8624097
G. Cosoli, S. Spinsante, F. Scardulla, L. D'Acquisto and L. Scalise, “Wireless ECG and cardiac monitoring systems: State of the art, available commercial devices and useful electronic components,” Measurement, vol. 177, art. no. 109243, Jun. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109243
S. M. Noor, E. John, and M. Panday, “Design and Implementation of an Ultralow-Energy FFT ASIC for Processing ECG in Cardiac Pacemakers,” IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 983-987, Apr. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2883642
A. L. Goldberger, L. A. Amaral, L. Glass, J. M. Hausdorff, et al., “PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals,” Circulation, vol. 101, no. 23, pp. e215–e220, 2000, doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
C. Kim, Y. H. Yun, K. Kim, and J. -Y. Seol, “Introduction to QAM-FBMC: From Waveform Optimization to System Design,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 54, no. 11, pp. 66-73, Nov. 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2016.1600384CM
C. -H. Heng and K. -H. Teng, “Reconfigurable, energy efficient transmitter with band-shaping and multi-channel support for biomedical applications,” in 2016 URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference (URSI AP-RASC), Seoul, Korea (South), 2016, pp. 986-989, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/URSIAP-RASC.2016.7601308
B. O. hAnnaidh, P. Fitzgerald, H. Berney, R. Lakshmanan, N. Coburn, S. Geary, B. Mulvey, “Devices and Sensors Applicable to 5G System Implementations,” in 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on 5G Hardware and System Technologies (IMWS-5G), Dublin, Ireland, 2018, pp. 1-3, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IMWS-5G.2018.8484316
T.-H. Tsai and W.-T. Kuo, “An Efficient ECG Lossless Compression System for Embedded Platforms With Telemedicine Applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 42207-42215, Jul. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2858857
N. Wang, J. Zhou, G. Dai, J. Huang, and Y. Xie, “Energy-Efficient Intelligent ECG Monitoring for Wearable Devices,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst., vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 1112-1121, Oct. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2930215
K. Nakatani, Y. Yamaguchi, Y. Komatsuzaki, S. Sakata, S. Shinjo, and K. Yamanaka, “A Ka-Band High Efficiency Doherty Power Amplifier MMIC using GaN-HEMT for 5G Application,” in 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on 5G Hardware and System Technologies (IMWS-5G), Dublin, Ireland, 2018, pp. 1-3, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IMWS-5G.2018.8484612
D. Lucani, G. Cataldo, J. Cruz, G. Villegas, and S. Wong, “A portable ECG monitoring device with Bluetooth and Holter capabilities for telemedicine applications,” in 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 2006, pp. 5244-5247, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260798
P. K. Singya, P. Shaik, N. Kumar, V. Bhatia, and M.-S. Alouini, “A Survey on Higher-Order QAM Constellations: Technical Challenges, Recent Advances, and Future Trends,” in IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc., vol. 2, pp. 617-655, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3067384
T. S. Rappaport, Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice, vol. 2. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice-Hall PTR, 1996.
F. Mazzenga, “Channel estimation and equalization for M-QAM transmission with a hidden pilot sequence,” IEEE Trans. Broadcast., vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 170-176, 2000, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/11.868934
J. G. Proakis and M. Salehi, Digital Communications, 2nd ed. NJ, USA: McGraw-Hill, Higher education, 2008.
“IEEE Standard for Telecommunications and Information Exchange Between Systems - LAN/MAN Specific Requirements - Part 11: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications: High Speed Physical Layer in the 5 GHz band,” in IEEE Std 802.11a-1999, pp.1-102, 1999, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.1999.90606
B. Abi-Saleh, B. Omar, “Einthoven’s Triangle Transparency: A Practical Method to Explain Limb Lead Configuration Following Single Lead Misplacements,” Rev. Cardiovasc. Med.,” vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 33–38, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.3909/ricm0506
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Una vez que el artículo es aceptado para su publicación en la RMIB, se les solicitará al autor principal o de correspondencia que revisen y firman las cartas de cesión de derechos correspondientes para llevar a cabo la autorización para la publicación del artículo. En dicho documento se autoriza a la RMIB a publicar, en cualquier medio sin limitaciones y sin ningún costo. Los autores pueden reutilizar partes del artículo en otros documentos y reproducir parte o la totalidad para su uso personal siempre que se haga referencia bibliográfica al RMIB. No obstante, todo tipo de publicación fuera de las publicaciones académicas del autor correspondiente o para otro tipo de trabajos derivados y publicados necesitaran de un permiso escrito de la RMIB.











