Specific Delineation Algorithm Based on Two-Stage EWMA for Noninvasive Estimation of Blood Pressure
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.46.1.1490Keywords:
algorithm, ABP, ECG, EWMA, PPGAbstract
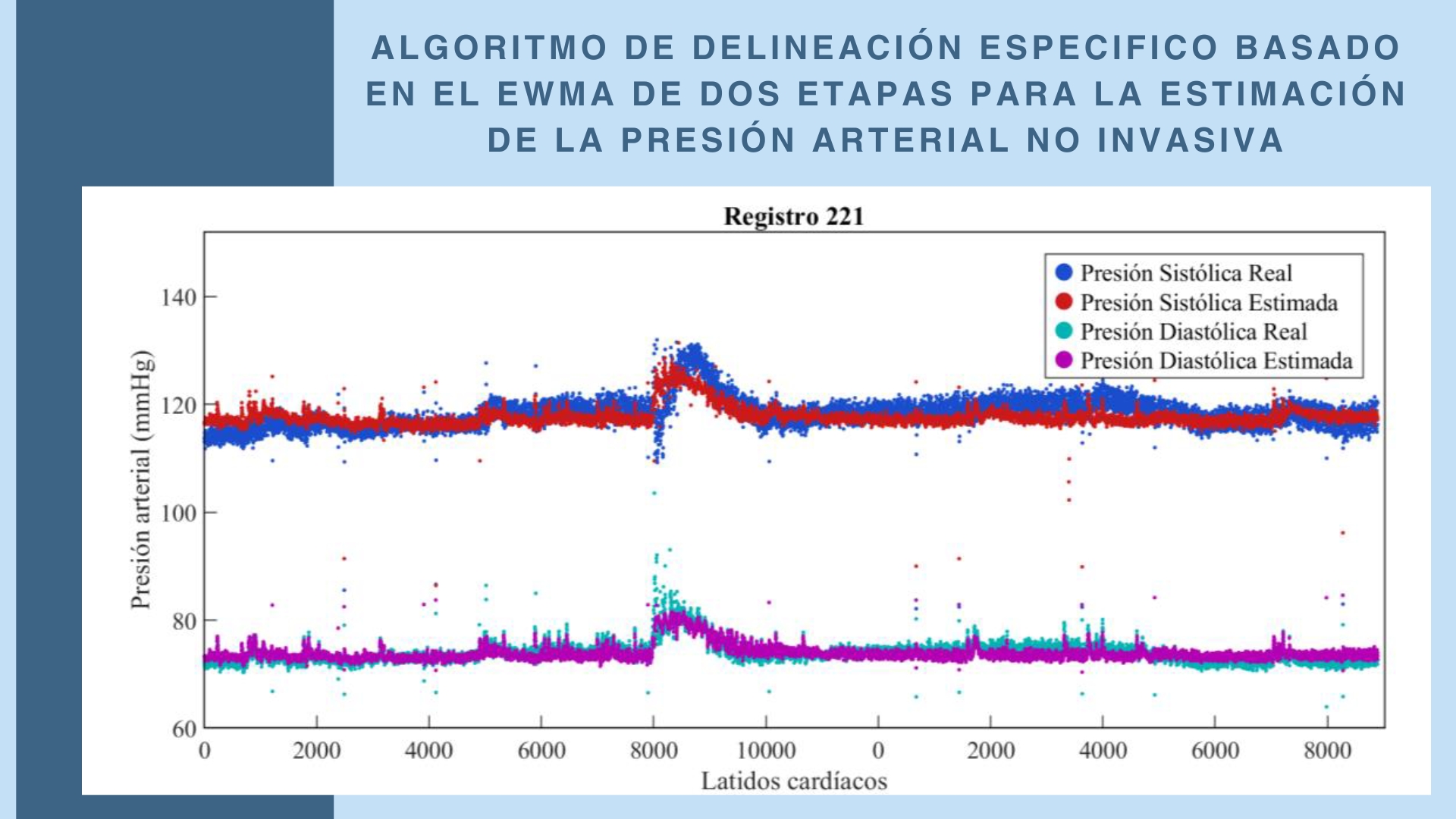
Dynamic noise, due to its variability and intensity, prevents conventional peak detection methods in ECG and PPG signals based on fixed thresholds from performing effectively in wearable devices. The inflexibility of these fixed thresholds results in low sensitivity and positive predictive value. Therefore, this study proposes a specific delineation algorithm with an adaptive threshold based on the Two-Stage Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) model, focusing on flexibility, precision, robustness against strong dynamic noise, and low computational load. The proposed algorithm demonstrated robust performance under high SNR conditions (24 dB and 18 dB), achieving 100 % sensitivity and positive predictive value. Under moderate noise conditions (12 dB), the algorithm maintained a high sensitivity of 99.39 % and a positive predictive value of 98.18 %, with a delineation error rate (DER) of 2.43 %. Even under low SNR conditions (6 dB), the algorithm significantly outperformed fixed-threshold-based approaches, which exhibited error rates exceeding 50 %. Furthermore, the algorithm was validated using a mathematical model to estimate blood pressure based on pulse transit time, with signals from the MIMIC database. The results showed a mean error of -1.422 mmHg for systolic blood pressure (SBP) and 0.577 mmHg for diastolic blood pressure (DBP), with standard deviations of 4.668 mmHg and 2.888 mmHg, respectively, meeting the standards of the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI).
Downloads
References
M. Kachuee, M. M. Kiani, H. Mohammadzade, M. Shabany, “Cuffless blood pressure estimation algorithms for continuous health-care monitoring,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 859–869, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2016.2580904
W. H. Lin et al., “Towards accurate estimation of cuffless and continuous blood pressure using multi-order derivative and multivariate photoplethysmogram features,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 63, 2021, art. no. 102198, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102198
O. Litvinova et al., “Patent landscape review of non-invasive medical sensors for continuous monitoring of blood pressure and their validation in critical care practice,” Front. Med., vol. 10, 2023, art. no. 1138051, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1138051
M. Salem et al., “Non-invasive data acquisition and IoT solution for human vital signs monitoring: Applications, limitations and future prospects,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 17, 2022, art. No. 6625, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176625
Y. Wang et al., “Recent advancements in flexible and wearable sensors for biomedical and healthcare applications,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., vol. 55, no. 13, 2022, art. no. 103002, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac3c73
A. Medina et al., “Continuous blood pressure estimation in wearable devices using photoplethysmography: A review,” Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng., vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 104-113, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.46338/ijetae1022_12
M. Y. M. Wong, E. Pickwell-MacPherson, Y. T. Zhang, J. C. Y. Cheng, “The effects of pre-ejection period on post-exercise systolic blood pressure estimation using the pulse arrival time technique,” Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., vol. 111, no. 1, pp. 135–144, 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1626-0
T. Vajanarat, A. Lek-uthai, “A comparison of cuff-less blood pressure estimation between pulse arrival time and pulse transit time using photoplethysmography,” en 17th Int. Conf. Electr. Eng./Electron., Comput., Telecommun. Inf. Technol. (ECTI-CON), Phuket, Tailandia, 2020, pp. 13–16, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTI-CON49241.2020.9158100
J. Cano, “Desarrollo de un método de estimación de la presión arterial combinando fotopletismografía y electrocardiografía,” Tesis de grado, Dept. Ing. Electron., Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, España, 2020. [En línea]. Disponible en: http://hdl.handle.net/10251/150068
F. S. Cattivelli, H. Garudadri, “Noninvasive cuffless estimation of blood pressure from pulse arrival time and heart rate with adaptive calibration,” en Proc. Int. 6th Workshop Wearable Implantable Body Sensor Netw., Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009, pp. 114-119, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/BSN.2009.35
J. M. Bote, J. Recas, R. Hermida, M. Díaz-Vicente, “Implementación de técnicas de estimación de la presión arterial a partir de ECG y PPG,” en I Jornadas de Computación Empotrada y Reconfigurable, Jornadas SARTECO (CEDI), Salamanca, España, 2016, pp. 551–559.
J. M. Bote et al., “A modular low complexity ECG delineation algorithm for real-time embedded systems,” IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform., vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 429–441, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2017.2671443
S. Nurmaini et al., “Robust electrocardiogram delineation model for automatic morphological abnormality interpretation,” Sci. Rep., vol. 13, 2023, art. no. 13736, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40965-1
J. Bote, “Algoritmos de monitorización de señales biomédicas en tiempo real para dispositivos portátiles de bajo consumo,” Tesis de Doctorado, Fac. Inform., Univ. Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, España, 2021. [En línea]. Disponible en: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.14352/5570
Z. Hao, X. Zhang, Z. Lai, “Adaptive R-peak detection algorithm based on brown exponential smoothing model,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 114355-114363, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3218308
X. Wan et al., “Electrocardiogram baseline wander suppression based on the combination of morphological and wavelet transformation based filtering,” Comput. Math. Methods Med., vol. 2019, no. 1, 2019, art. no. 196156, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7196156
F. R. Hashim et al., “Electrocardiogram noise cancellation using wavelet transform,” J. Fundam. Appl. Sci., vol. 9, no. 3S, pp. 131-140, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v9i3s.11
Md. A. Kabir, C. Shahnaz, “Denoising of ECG signals based on noise reduction algorithms in EMD and wavelet domains,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 481–489, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2011.11.003.
Y. Hong, Y. Lian, “A Memristor-based continuous-time digital FIR filter for biomedical signal processing,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Papers, vol. 62, no. 5, pp. 1392-1401, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2015.2403033.
J. Pan, W. J. Tompkins, “A real-time QRS detection algorithm,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. BME-32, no. 3, pp. 230–236, 1985, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.1985.325532
J. A. Van Alste, T. S. Schilder, “Removal of base-line wander and power-line interference from the ECG by an efficient FIR filter with a reduced number of taps”, IEEE Trans. Biomédica. Ing., vol. 32, no. 12, pp. 1052-1060, 1985, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.1985.325514
J. Park, S. Lee, U. Park, “R peak detection method using wavelet transform and modified Shannon energy envelope,” J. Healthc. Eng., vol. 2017, 2017, art. no. 4901017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4901017
K. Krishnakumar, S. Latha, “Different methods to remove baseline wandering noise from the ecg signal: a research perspective,” en Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Smart Energy (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIS56108.2023.10073914
T. N. Nguyen, T. H. Nguyen, B. V. Ngo, “R peak determination using a WDFR algorithm and adaptive threshold,” Appl. Comput. Sci., vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 19-30, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.35784 /acs -2022 -18
T. Rodrigues, S. Samoutphonh, H. Silva, A. Fred, “A low-complexity R-peak detection algorithm with adaptive thresholding for wearable devices,” en 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italia, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9413245
M. Shahbakhti et al., “Fusion of EEG and eye blink analysis for detection of driver fatigue,” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., vol. 31, pp. 2037–2046, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3267114
J. Arteaga-Falconi, H. Al Osman, A. El Saddik, “R-peak detection algorithm based on differentiation,” en Proc. 2015 IEEE 9th Int. Symp. Intell. Signal Process. (WISP), Siena, Italia, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/WISP.2015.7139147
PCP Chao et al., “Machine learning leading cuffless PPG blood pressure sensors into the next stage,” IEEE Sens. J., vol. 21, no.11, pp. 12498–12510, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3073850
H. Tan et al., “Heartbeat-aware convolutional neural network for R-peak detection of wearable device ECG data,” J. South. Med. Univ., vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 375–383, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.03.09
L. Khriji, A. M. Al-Busaidi, "New adaptive thresholding-based ECG R-peak detection technique," en Proc. IEEE Middle East Conf. Biomed. Eng. (MECBME), Túnez, Túnez, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MECBME.2018.8402423
A. Hamed, S. Saeid, M. Karim, “A novel signal segmentation method based on standard deviation and variable threshold,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 27-34, 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.5120/4073-5860
M. Niaz, M. Khan, “Pan-Tompkins: a robust approach to detect R-peaks in ECG signals,” en Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Bioinf. Biomed. (BIBM), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2022, pp. 2905-2912, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM55620.2022.9995552
J. Yu, S. B. Kim, J. Bai, S. W. Han, “Comparative study on exponentially weighted moving average approaches for the self-starting forecasting,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 20, 2020, no. art. 7351, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207351
P. R. Winters, “Forecasting sales by exponentially weighted moving averages,” Manage. Sci., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 324–342, 1960. [En línea]. Disponible en: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2627346.
T. Andrasto et al., “Method EWMA (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average) as a filter to fine and remove noise on time series data,” en 11th Engineering International Conference: Applied Green Technology for Environment Conservation Through Continous Engineering (EIC 2022)., Indonesia, 2023, art. no. 012012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1203/1/012012
A. D. Little, R. G. Brown. (1956). Exponential smoothing for predicting demand. [En línea]. Disponible: https://www.industrydocuments.ucsf.edu/docs/jzlc0130
G. T. Wilson, “Book review: time series analysis: forecasting and control, 5th edition, by George E. P. Box, Gwilym M. Jenkins, Gregory C. Reinsel and Greta M. Ljung, 2015. Published by John Wiley and Sons Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, pp. 712. ISBN: 978-1-118-67502-1,” J. Time Ser. Anal., vol. 37, pp. 709-711, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsa.12194
V. Akgiray, “Conditional heteroscedasticity in time series of stock returns: evidence and forecasts,” J. Bus., vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 55–80, 1989, doi: http://doi.org/10.1086/296451
M. W. Watson, “Chapter 47 Vector autoregressions and cointegration,” in Handbook of Econometrics, 1994, pp. 2843–2915, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1573-4412(05)80016-9
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature, vol. 521, págs. 436–444, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
P. Jarrín, J. Xavier, “Comparación entre varios métodos de pronósticos basados en series de tiempo para predecir la demanda de placas digitales en empresas del sector gráfico quiteño desde el año 2009 hasta el año 2015,” Tesis de maestría, Facultad de Ciencias Administrativas, Escuela Politécnica Nacional, Ecuador, 2015. [En línea]. Disponible en: http://bibdigital.epn.edu.ec/handle/15000/17016
R. Huamani et al., “Implementation of a real-time 60 Hz interference cancelation algorithm for ECG signals based on ARM Cortex M4 and ADS1298,” en Proc. IEEE 24th Int. Congress on Electron. Elect. Eng. Comput. (INTERCON), Cusco, Peru, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/INTERCON.2017.8079725
E. Supo et al., “PRD as an indicator proposal in the evaluation of ECG signal acquisition prototypes in real patients,” Technol. Innov. Andean Ind., Barranquilla, Colombia, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ANDESCON56260.2022.9989674
C. Huisa et al., “PCG heart sounds quality classification using neural networks and SMOTE Tomek links for the think health project,” en Proc. Data Anal. Manag. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst., A. Khanna, Z. Polkowski, O. Castillo, Eds. 2023, vol. 572, pp. 803-811, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7615-5_65
R. Sulla, J. Talavera, E. Supo, A. Montoya, “Non-invasive glucose monitor based on electric bioimpedance using AFE4300,” en Proc. IEEE 26th Int. Conf. Electron., Elect. Eng. Comput. (INTERCON), Lima, Peru, 2019, doi: https://10.1109/INTERCON.2019.8853561
J. M. Bote, J. Recas, R. Hermida, “Evaluation of blood pressure estimation models based on pulse arrival time,” Comput. Elect. Eng., vol. 84, 2020, no. art. 106616, doi: 10.1016 /j.compeleceng.2020.106616
A. Johnson, T. Pollard, R. Mark, 2016, “MIMIC-III Clinical Database (1.4 version),” PhysioNet, doi: https://doi.org/10.13026/C2XW26
I. Silva, G. Moody, “An open-source toolbox for analysing and processing PhysioNet databases in MATLAB and Octave”, J. Open Res. Softw., vol. 2, no. 1, 2014, no. art. e27, doi: 10.5334/jors.bi
A. H. Sayed, Fundamentals of Adaptive Filtering, Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley, 2003.
P. Laguna, R. Mark, A. Goldberg, G. Moody, “A database for evaluation of algorithms for measurement of QT and other waveform intervals in the ECG,” en Conf. Comput. Cardiol. 1997, Lund, Suecia, 1997, pp. 673–676, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CIC.1997.648140
A. Johnson et al., “MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database,” Scientific Data, vol. 3, 2016, no. art. 60035, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.35
A. Goldberger et al., “PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet : components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals,” Circulation, vol. 101, no. 23, pp. e215–e220, 2000, doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215
D. J. Hughes, C. F. Babbs, L. A. Geddes, J. D. Bourland, “Measurements of Young's modulus of elasticity of the canine aorta with ultrasound,” Ultrason. Imag., vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 356-367, 1979, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0161-7346(79)90028-2
W. Chen et al., “Continuous estimation of systolic blood pressure using the pulse arrival time and intermittent calibration,” Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., vol. 38, pp. 569-574, 2000, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345755
P. K. Baheti, H. Garudadri, “Heart rate and blood pressure estimation from compressively sensed photoplethysmograph,” en Proc. 4th Int. ICST Conf. on Body Area Netw., Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.4108/ICST.BODYNETS2009.6023
C. C. Y. Poon, Y. T. Zhang, “Cuff-less and Noninvasive Measurements of Arterial Blood Pressure by Pulse Transit Time,” en Proc. 27th Annu. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Conf., vol. 6, Shanghai, China, 2006, pp. 5877–5880, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2005.1615827
C. P. Chua, C. Heneghan, “Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring using ECG and Finger Photoplethysmogram,” en Proc. 2006 Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., NY, USA, 2006, pp. 5117–5120, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2006.259612
P. Fung et al., “Continuous noninvasive blood pressure measurement by pulse transit time,” en Proc. 26th Ann. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004, pp. 738–741, doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1403264
A. A. Awad et al., “How Does the Plethysmogram Derived from the Pulse Oximeter Relate to Arterial Blood Pressure in Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Patients?,” Anesth. Analg., vol. 93, no. 6, pp. 1466–1471, 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000539-200112000-00022
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Upon acceptance of an article in the RMIB, corresponding authors will be asked to fulfill and sign the copyright and the journal publishing agreement, which will allow the RMIB authorization to publish this document in any media without limitations and without any cost. Authors may reuse parts of the paper in other documents and reproduce part or all of it for their personal use as long as a bibliographic reference is made to the RMIB. However written permission of the Publisher is required for resale or distribution outside the corresponding author institution and for all other derivative works, including compilations and translations.







