Using Machine Learning Algorithms on Electroencephalographic Signals to Assess Engineering Students' Focus While Solving Math Exercises
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.44.4.2Keywords:
attention measurement, brain-computer interface, classification, electroencephalographic signals, machine learning, mathAbstract
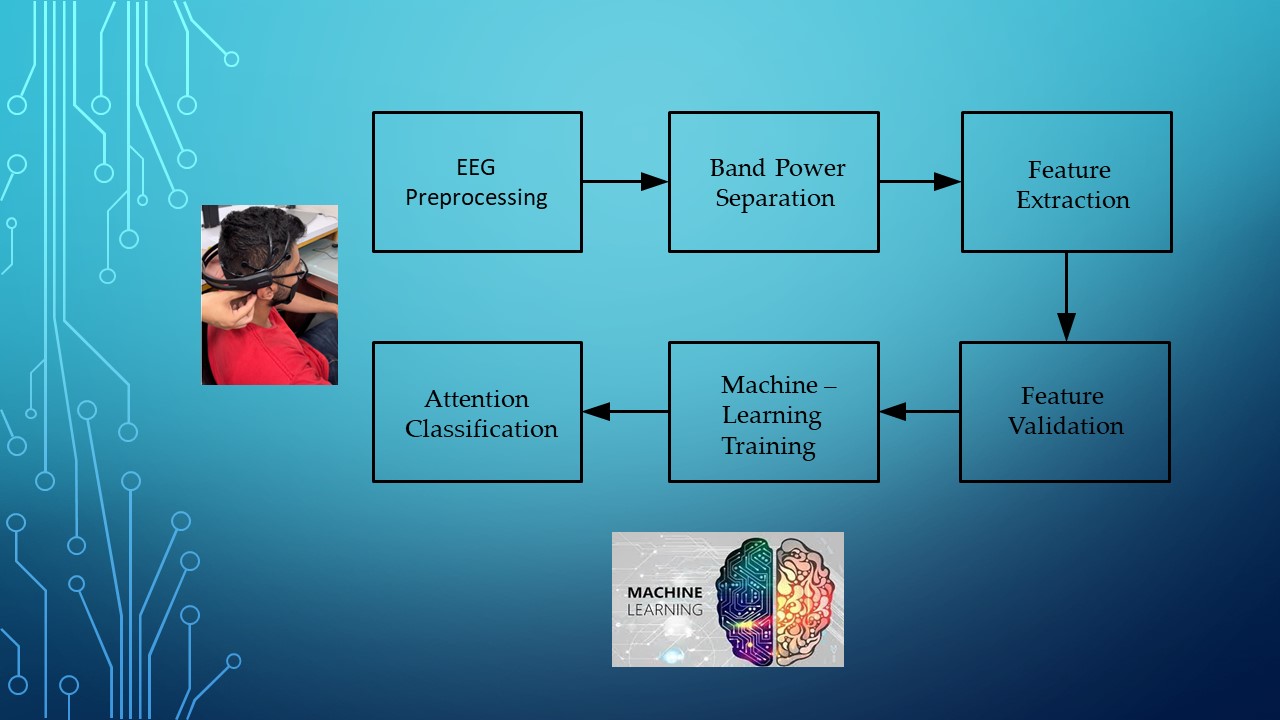
In this paper, we present an attention classification method using Machine-Learning Algorithms. The EEG signals were recorded from ten engineering students with an EPOC+BCI using the electrodes F3, F4, P7, and P8 while solving some mathematical operations. The recording time for these activities is around 20 minutes. Next, a similar time EEG register is obtained while doing non-academic activities, such as chattering with the staff, checking cell phones, or playing a video game. With these EEG registers, we obtained a set of features to train and evaluate attention using Machine Learning algorithms. This research shows how engineering students interact with math topics in solving mental operations and complex reasoning by increasing brain domain and knowledge for mathematical reasoning-related processes, such as sustained and shifting attention and logical constructions for object interaction during operations resolution. The Random Forest algorithm (RF) obtained the highest accuracy with 0.7392, an F1 Score of 0.7430, and the highest Specificity/Accuracy with 0.7261.
Downloads
References
E. Levin, J. Bernier, “Attention Span,” in Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development, S. Goldstein, J. A. Naglieri, Eds. New York, U. S.: Springer, 2011, pp. 163, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9_22
M. A. Rasheed, P. Chad, S. Ahmed, H. Sharif, Z. Hoodbhoy, A. Siddiqui, B. S. Hasan, “Use of artificial intelligence on Electroencephalogram (EEG) waveforms to predict failure in early school grades in children from a rural cohort in Pakistan,” PLoS One, vol. 16, no. 2, art. no. e0246236, Feb. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0246236
PLoS One, “Correction: Use of artificial intelligence on Electroencephalogram (EEG) waveforms to predict failure in early school grades in children from a rural cohort in Pakistan,” PLoS One, vol. 16, no. 2, art. no. e0247744, Feb. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0247744
M. F. Mavilidi, K. Ouwehand, N. Riley, P. Chandler, F. Paas, “Effects of An Acute Physical Activity Break on Test Anxiety and Math Test Performance,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 17, no. 5, art. no. 1523, Feb. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390%2Fijerph17051523
M. Hartmann, J. Laubrock, M. H. Fischer, “The visual number world: A dynamic approach to study the mathematical mind,” Q. J. Exp. Psychol., vol. 71, no. 1, Jan. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2016.1240812
W. Auccahuasi, C. Ovalle, Z. Ayvar, J. Aybar, et al., “Methodology to evaluate the levels of attention and meditation in the development of virtual classes through BCI devices,” in Workshop Technol. Innov. Edu. Knowledge Dissemination CEUR-WS, Goa, India, 2021, pp. 51-60. [Online]. Available: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2869/PAPER_06.pdf
S. M. Manjur, M.-B. Hossain, P. A. Constable, D. A., Thompson, et al., “Detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Spectral Analysis of Electroretinogram and Machine Learning: Preliminary results,” 2022 44th Ann. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. (EMBC), Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom, 2022, pp. 3435-3438, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9871173
B. Ari, N. Sobahi, Ö. F. Alçin, A. Sengur, U. R. Acharya, “Accurate detection of autism using Douglas-Peucker algorithm, sparse coding based feature mapping and convolutional neural network techniques with EEG signals,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 143, art. no. 105311, Apr. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105311
A. Shoeibi, M. Rezaei, N. Ghassemi, Z. Namadchian, A. Zare, J. M. Gorriz, “Automatic Diagnosis of Schizophrenia in EEG Signals Using Functional Connectivity Features and CNN-LSTM Model,” in Artif. Intell. Neurosc. Affective Analysis and Health Applications (IWINAC 2022). J. M. Ferrández Vicente, J. R. Álvarez-Sánchez, F. de la Paz López, H. Adeli, Eds. Puerto de la Cruz, Tenerife, Spain, 2022, pp. 63-73, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06242-1_7
F. J. Alvarado-Rodríguez, K. P. Ibarra-González, C. Eccius-Wellmann, H. Vélez-Pérez, R. Romo-Vázquez, “Electrophysiological Brain Response to Error in Solving Mathematical Tasks,” Mathematics 2022, vol. 10, no. 18, art. no. 3294, Sep. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183294
J. J. Esqueda-Elizondo, R. Juárez-Ramírez, O. R. López-Bonilla, E. E. García-Guerrero, et al., “Attention Measurement of an Autism Spectrum Disorder User Using EEG Signals: A Case Study,” Math. Comput. Appl., vol. 27, no. 2, art. no. 21, Mar. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/mca27020021
F. Fahimi, C. Guan, W. B. Goh, K. K. Ang, C. G. Lim, T. S. Lee, “Personalized features for attention detection in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder,” in 2017 39th Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. (EMBC), Jeju, Korea (South), Jul. 2017, pp. 414–417, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2017.8036850
K. H. Khng, R. Mane, “Beyond BCI—Validating a wireless, consumer-grade EEG headset against a medical-grade system for evaluating EEG effects of a test anxiety intervention in school,” Adv. Eng. Inform., vol. 45, art. no. 101106, Aug. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2020.101106
I. A. Fouad, “A robust and reliable online P300-based BCI system using Emotiv EPOC + headset,” J. Med. Eng. Technol., vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 94–114, Feb. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/03091902.2020.1853840
N. V. Dubrovinskaya, R. I. Machinska, Y. V. Kulakovsky, “Brain Organization of Selective Tasks Preceding Attention: Ontogenetic Aspects,” in Complex Brain Functions, R. Miller, A. M. Ivantsky, Eds. Boca Ratón, FL, USA: CRC Press, 2000, ch. 9 pp. 169–180. doi: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203304785
N. V. Dubrovinskaya, R. I. Machinskaya, “Reactivity of θ and α EEG Frequency Bands in Voluntary Attention in Junior Schoolchildren,” Hum. Physiol., vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 522-527, Sep. 2002, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1023%2FA%3A1020266516114
Emotiv Inc., Frequency Bands - EmotivPRO v3.0, (2020). Accessed: Nov. 2021. [Online]. Available: https://emotiv.gitbook.io/emotivpro-v3/data-streams/frequency-bands
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Upon acceptance of an article in the RMIB, corresponding authors will be asked to fulfill and sign the copyright and the journal publishing agreement, which will allow the RMIB authorization to publish this document in any media without limitations and without any cost. Authors may reuse parts of the paper in other documents and reproduce part or all of it for their personal use as long as a bibliographic reference is made to the RMIB. However written permission of the Publisher is required for resale or distribution outside the corresponding author institution and for all other derivative works, including compilations and translations.







