Web-based Interactive 3D Modeling and Visualization of the Human Brain towards Anatomy Education
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.45.3.5Keywords:
3D human brain, Web-based 3D brain, 3D medical imaging, Web-based anatomy learning, 3D modeling and visualizationAbstract
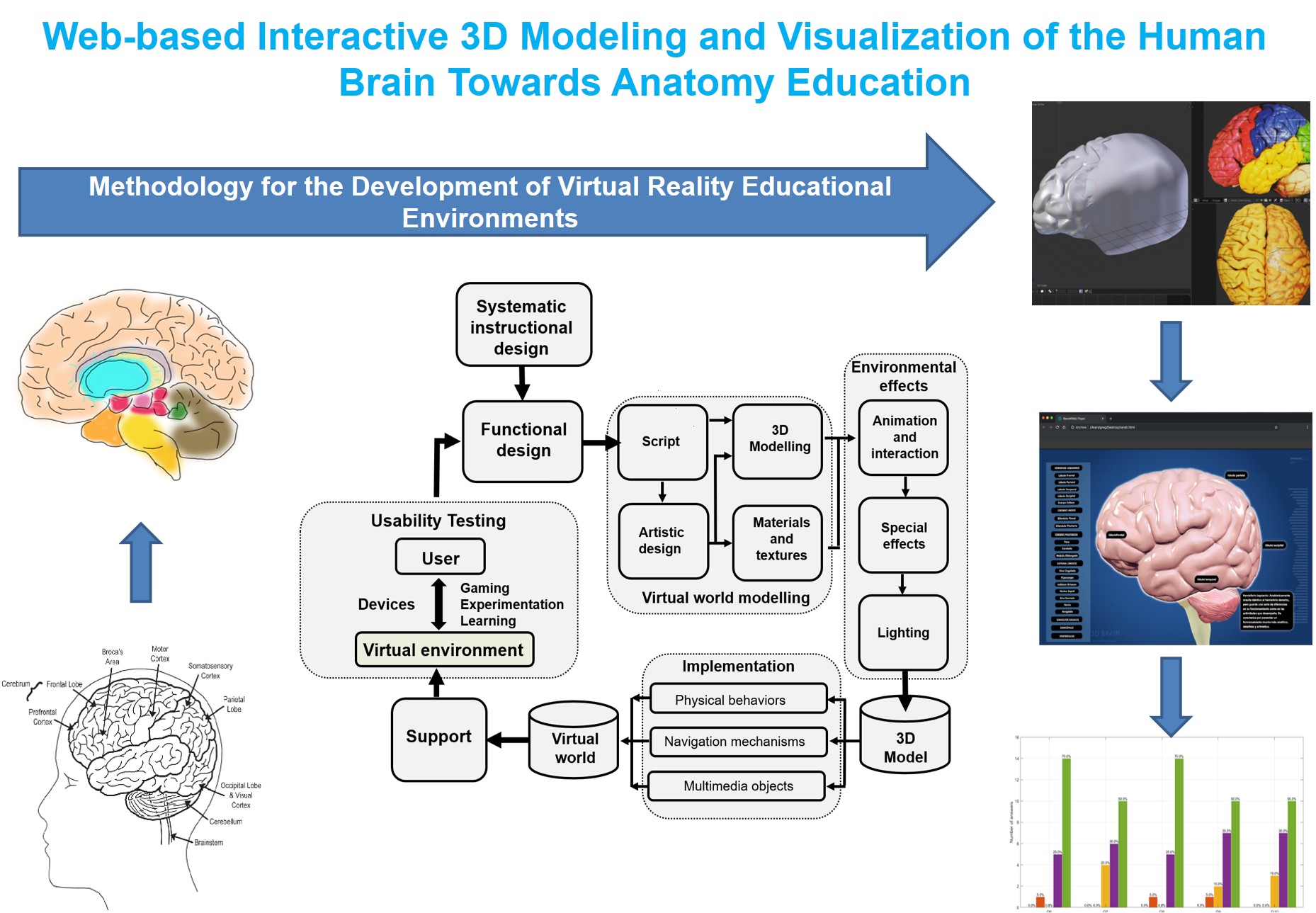
Today, visualization of 3D medical images is an essential tool for medical education. Web-based 3D tools for the teaching-learning process have turned out to be an efficient alternative to conventional systems. In this work, we aim the modeling process and 3D web-based interactive visualization of the human brain using 3D web technologies and an improvement of the Methodology for the Development of Virtual Reality Educational Environments (MEDEERV, for its acronym in Spanish). 20 undergraduate medicine, dentistry, gerontology, and computer science students performed a brain model usability test (9 women; 11 men, mean age = 22.1 years, SD = 0.70). To this end, we used a post-test questionnaire with Likert scale answers whose alpha of Cronbach was 0.93.
The proof of concept of the brain model that we have developed in this work provides evidence of the viability of the system to be used as a web tool for basic neuroanatomy learning. The main contribution of this work focuses on the implementation of MEDEERV to model the 3D human brain, plus the usability testing for reengineering feedback. This approach to modeling, visualizing, and evaluating could be used in other areas of human anatomical teaching. Although the experimental results show a good user experience, functionality and usability, it is necessary to generate a new version and carry out a study with a larger and more specific population with knowledge of brain anatomy.
Downloads
References
E. Alim, Ö. Coskun and T. V. Peker, “Comparison and Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Traditional
Neuroanatomy Teaching in Medical Education with Virtual-Reality Application Based On 3D Virtual,” Gazi
Med. J., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 407-415, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.12996/gmj.2024.4191
I. D. Keenan and A. Ben Awadh, “Integrating 3D visualisation technologies in undergraduate anatomy
education,” Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., no. 1120, pp. 39-53, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06070-1_4
M. A. Javaid, S. Chakraborty, J. Cryan, H. Schellekens and A. Toulouse, “Understanding neurophobia: Reasons
behind impaired understanding and learning of neuroanatomy in cross‐disciplinary healthcare students,” Anat.
Sci. Educ., no. 11, pp. 81-93, 2028, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1711
C. Ekstrand, A. Jamal, R. Nguyen, A. Kudryk, J. Mann and I. Mendez, “Immersive and interactive virtual
reality to improve learning and retention of neuroanatomy in medical students: a randomized controlled study,”
CMAJ Open, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 103-109, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.9778/cmajo.20170110
F. Nicolosi, F. Pessina, C. A. Gelmi, F. Belott, D. E. Mahoney, E. Agosti and G. Spena, “New neuroanatomy
learning paradigms for the next generation of trainees: a novel literature-based 3D methodology,” Clin. Neurol.
Neurosurg., vol. 210, 2021, art. no. 106948, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106948
M. V. Petersen, J. Mlakar, S. Haber, M. Parent, Y. Smith, P. L. Strick and M. A. Griswold, “Holographic
reconstruction of axonal pathways in the human brain,” Neuron, vol. 104, no. 6, pp. 1056-1064, 2019, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.09.030
S. B. Tomlinson, B. k. Hendricks and A. Cohen-Gadol, “Immersive three-dimensional modeling and virtual
reality for enhanced visualization of operative neurosurgical anatomy,” World Neurosurg., vol. 131, pp. 313-
, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.06.081
I. D. Keenan and A. Ben Awadh, “Biomedical Visualisation . Advances in Experimental Medicine and
Biology,” in Integrating 3D Visualisation Technologies in Undergraduate Anatomy Education, P. M. Rea, Ed.,
vol. 1120, Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2019, ch. 4, pp. 39-53, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06070-
_4
L. Zhou, M. Fan, C. Hansen, C. Johnson and D. Weiskopf, “A Review of Three-Dimensional Medical Image
Visualization,” Health Data Sci., vol. 2022, 2022, art. no. 9840519, doi: https://doi.org/10.34133/2022/9840519
H. Aerts, M. Schirner, T. Dhollander, B. Jeurissen, et al., “Modeling brain dynamics after tumor resection using
The Virtual Brain,” Neurolmage, vol. 213, 2020, art. no. 116738, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116738
L. T. De Paolis, A. De Mauro, J. Raczkowsky and G. Aloisio, “Virtual Model of the Human Brain for
Neurosurgical Simulation,” Stud. Health Techonol. Inform., vol. 150, pp. 811-815, 2009, doi:
https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-811
B. Fiani, F. De Stefano, A. Kondilis, C. Covarrubias, L. Reier and K. Sarhadi, “Virtual reality in neurosurgery:
"can you see it?"-A review of the current applications and future potential,” World Neurosurg., vol. 141, pp.
-298, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.06.066
O. Hellum, Y. Mu, M. Kersten-Oertel and Y. Xiao, “A novel prototype for virtual-reality-based deep brain
stimulation trajectory planning using voodoo doll annotation and eye-tracking,” Comput. Methods Biomech.
Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 418-424, 2022, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2021.1997645
Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Biomédica
O. Hellum, C. Steele and Y. Xiao, “SONIA: an immersive customizable virtual reality system for the education
and exploration of brain networks,” Front. Virtual Real., vol. 4, 2024, art. no. 2023, doi:
https://doi.org/10.3389/frvir.2023.1244096
K. B. Schloss, M. A. Schoenlein, R. Tredinnick, S. Smith, et al., “The UW virtual brain project: an immersive
approach to teaching functional neuroanatomy,” Transl. Issues Psychol. Sci., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 297-314, 2021,
doi: https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/tps0000281
S. K. Taswell, T. Veeramacheneni and C. Taswell, “BrainWatch software for interactive exploration of brain
scans in 3D virtual reality systems,” in 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society, Jeju, Korea (South), 2017, pp. 3704-3707, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2017.8037662
J. J. G. Keiriz, L. Zhan, O. Ajilore, A. D. Leow and A. G. Forbes, “NuroCave: A web-based immersive
visualization platform for exploring connectome datasets,” Netw. Neurosci., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 344-361, 2018,
doi: https://doi.org/10.1162%2Fnetn_a_00044
D. J. Henssen, L. van den Heuvel, G. V. De Jong, M. A. Vorstenbosch, A. M. van Cappellen van Walsum, M.
M. Van den Hurk and R. H. Bartels, “Neuroanatomy learning: Augmented reality vs. cross‐sections,” Anat.
Sci. Educ., vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 353-365, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1912
Q. Yuan, X. Chen, J. Zhai, Y. Chen, et al. “Application of 3D modeling and fusion technology of medical
image data in image teaching,” BMC Med. Educ., vol. 21, no. 1, 2021, art. no. 194, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02620-z
O. Hellum, M. Kersten-Oertel and Y. M. Xiao, “Assessment of user interaction strategies for neurosurgical data
navigation and annotation in virtual reality,” Virtual Real., vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 1345-1355, 2022, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-022-00740-5
S. Soobia , N. Jhanjhi, N. Mehmod and H. Mamoona, “Analysis of Software Development Methodologies,” Int.
J. Comput. Dig. Syst., vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 446-460, 2019, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/ijcds/080502
J. Polcar, M. Gregor, P. Horejsi, and P. Kopecek, “Methodology for designing virtual reality applications,” in
th International DAAAM Symposium, Zadar, Croatia, 2016.
G. A. Torres-Samperio, A. Franco-Arcega, M. J. Gutiérrez-Sánchez and A. Suárez-Navarrete, “Metodologia
para el modelado de sistemas de realidad virtual para el aprendizaje en dispositivos móviles,” Pistas Edu., vol.
, no. 127, pp. 518-534, 2018. [Online]. Available:
https://pistaseducativas.celaya.tecnm.mx/index.php/pistas/article/view/1054
J. R. Burger, “Human Brain anatomy,” in Human Memory Modeled with Standard Analog and Digital Circuits:
Inspiration for Man-made Computers, USA: Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2009, pp. 301-308.
C. M. Barnum, Usability testing essentials: Ready, set... test!, 2nd ed., Cambridge, MA, USA: Elsevier, 2020,
pp. 197-246.
J. Lewis, “Sample sizes for usability studies: Additional considerations,” Hum. Factors, vol. 36, no. 2, p.
–378, 1994, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/001872089403600215
J. Nielsen and T. Landauer, “A mathematical model of the finding of usability problems,” in CHI '93:
Proceedings of the INTERACT '93 and CHI '93 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
Amsterdam, 1993, pp. 206-213, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/169059.169166
R. A. Virzi, “Refining the test phase of the usability evaluation: How many subjects is enough?,” Hum. Factors,
vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 457–468, 1992, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/001872089203400407
Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Biomédica
B. Albert and T. S. Tullis, Measuring the user experience: Collecting, analyzing, and presenting UX metrics,
Cambridge, MA, USA: Elsevier, 2022.
V. Herrera-Tirado, J. Albusac-Jimenez, C. Gonzalez-Morcillo, R. Perales-Gomez, L. Blanco-Coloma, S.
Ceruelo-Abajo and A. D. Reyes Guzman, “Valoración de la Experiencia del Usuario en Entornos Virtuales de
Rehabilitación de Miembros Superiores,” in XLI Congreso Anual de la Sociedad Española de Ingeniería
Biomedica, Cartagena, Colombia, 2023, pp. 157-160.
S. Settapat, T. Achalakul and M. Ohkura, “The usability evaluation of web-based 3D medical image
visualization. In Design, User Experience, and Usability. Theory, Methods, Tools and Practice,” in First
International Conference, DUXU 2011, Held as Part of HCI International 2011, Orlando, FL, USA, 2011, pp.
-516, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21708-1_57
S. Settapat, T. Achalakul and M. Ohkura, “Web‐based 3D medical image visualization framework for
biomedical engineering education,” Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ., vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 216-226, 2014, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.20548
A. Joshi, S. Kale, S. Chandel and D. K. Pal, “Likert Scale: Explored and Explained,” Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol.,
vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 396-403, 2015. [Online]. Available:
Universidad de Valencia. (2022). Apuntes de estimación de la fiabilidad de consistencia interna de los ítems de
un instrumento de medida. [Online]. Available: https://www.uv.es/~friasnav/AlfaCronbach.pdf
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Upon acceptance of an article in the RMIB, corresponding authors will be asked to fulfill and sign the copyright and the journal publishing agreement, which will allow the RMIB authorization to publish this document in any media without limitations and without any cost. Authors may reuse parts of the paper in other documents and reproduce part or all of it for their personal use as long as a bibliographic reference is made to the RMIB. However written permission of the Publisher is required for resale or distribution outside the corresponding author institution and for all other derivative works, including compilations and translations.







